What Is a Blockchain?
Like a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in a digital format. The difference between a typical database and a blockchain is how the data is structured.
A blockchain is a distributed database or (ledger) that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. Like a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in a digital format. The difference between a typical database and a blockchain is how the data is structured.
A blockchain collects information together in groups, known as blocks, that hold sets of information. Blocks have certain storage capacities and, when filled, are closed and linked to the previously filled block, forming a chain of data known as the blockchain.
When data is recorded in a blockchain, it's nearly impossible to change or remove it. This is because if one block in one chain was changed, it would be immediately apparent it had been tampered with. If hackers wanted to corrupt a blockchain system, they would have to change every block in the chain across all of the distributed versions of the chain.
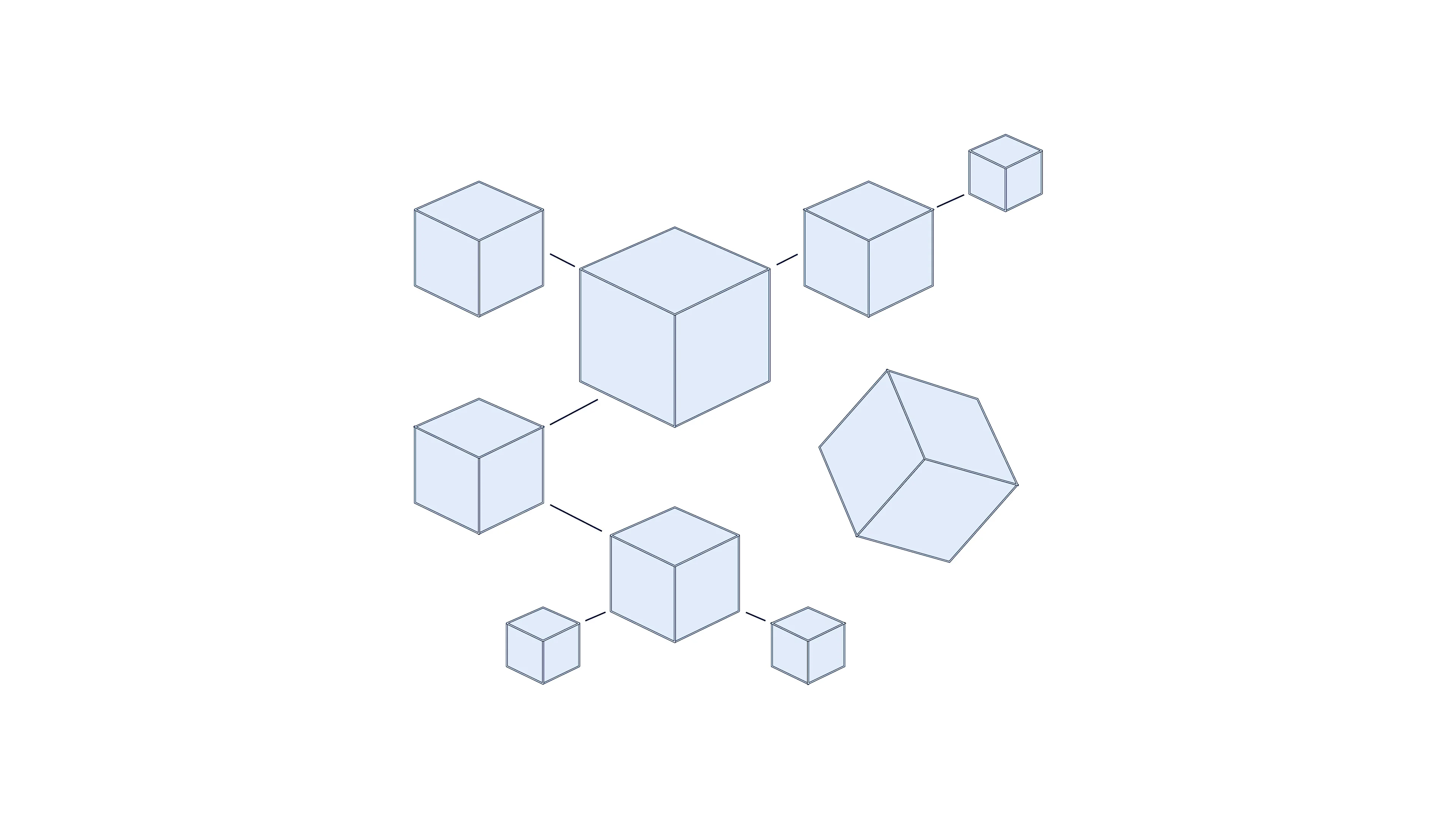
Blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are constantly and continually growing as blocks are being added to the chain, which significantly adds to the security of the ledger.
Transactions on a blockchain are typically economic, like cryptocurrencies, but we can store any kind of information in the blocks.